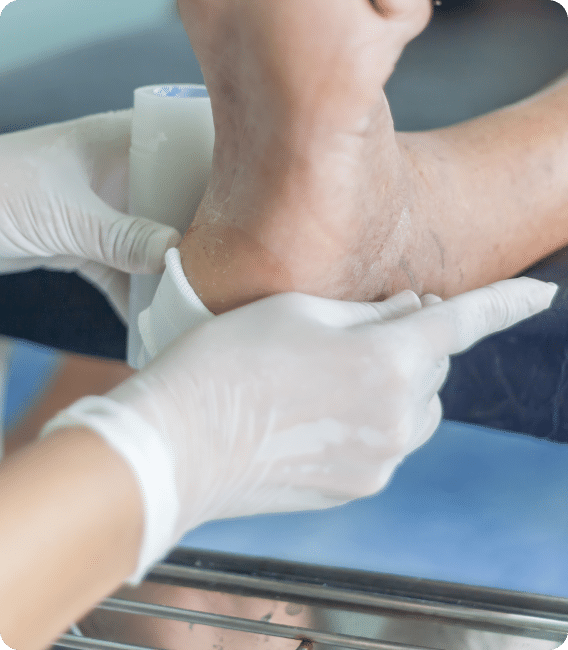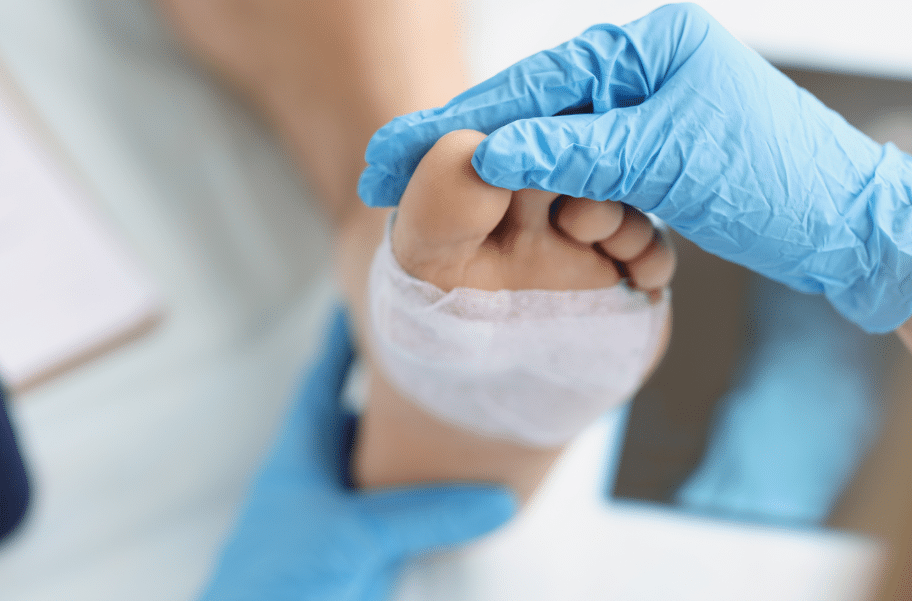
Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Understanding Diabetic Foot Ulcers and Their Treatment
What are Diabetic Foot Ulcers?
Diabetic foot ulcers are open sores or wounds that develop on the feet of individuals with diabetes. They are a common complication of diabetes and typically occur due to a combination of factors, including neuropathy (nerve damage), peripheral arterial disease (poor blood circulation), and impaired wound healing.
Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcers
The treatment of diabetic foot ulcers requires a multidisciplinary approach aimed at promoting wound healing, preventing infection, and reducing the risk of complications.
- Debridement: Removal of dead or infected tissue from the ulcer to promote healing and reduce the risk of infection. Debridement can be performed using various methods, including surgical, mechanical, enzymatic, or autolytic.
- Wound Dressings: Application of appropriate wound dressings to maintain a moist wound environment, absorb excess exudate, and protect the ulcer from further injury. Dressings may include hydrocolloids, foams, hydrogels, alginates, or antimicrobial dressings, depending on the characteristics of the ulcer.
- Offloading: Offloading pressure from the affected area to reduce friction and promote healing. This may involve the use of specialized footwear, orthotic devices, total contact casts, or other offloading modalities to redistribute pressure away from the ulcer.
- Offloading: Offloading pressure from the affected area to reduce friction and promote healing. This may involve the use of specialized footwear, orthotic devices, total contact casts, or other offloading modalities to redistribute pressure away from the ulcer.
- Wound Cultures: Collection of tissue samples from the ulcer for laboratory analysis to identify the causative organisms and guide antibiotic selection.
- Vascular Evaluation: Assessment of blood flow to the feet and legs to identify peripheral arterial disease (PAD) or other vascular complications that may impair wound healing. Vascular interventions such as angioplasty or bypass surgery may be necessary to improve blood flow to the affected area.
- Optimal Glycemic Control: Maintenance of tight blood sugar control to promote wound healing and reduce the risk of infection. This may involve adjustments to diet, medication, or insulin therapy under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
- Foot Care Education: Education on proper foot care practices, including daily inspection of the feet, wearing appropriate footwear, keeping the feet clean and moisturized, and avoiding activities that may increase the risk of injury.
- Self-Monitoring: Teaching patients how to monitor their foot health and recognize signs of complications, such as changes in skin color, temperature, or sensation.
- Revascularization: Surgical procedures to restore blood flow to the affected area in cases of severe peripheral arterial disease.
- Amputation: In cases where conservative measures fail or complications are severe, surgical amputation of the affected toe, foot, or lower extremity may be necessary to prevent the spread of infection and preserve overall health and mobility.
- Collaborative Care Team: Involvement of a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals, including podiatrists, vascular surgeons, wound care specialists, endocrinologists, and infectious disease specialists, to provide comprehensive care and support for patients with diabetic foot ulcers.
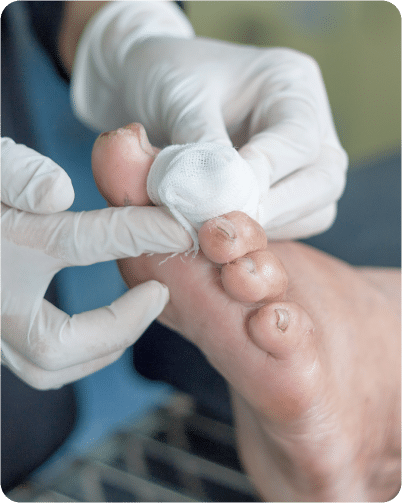
When to Seek Medical Attention?

Seeking prompt medical attention is crucial if you have diabetic foot ulcers, as early intervention can help prevent complications and promote healing. Here are situations when it’s advisable to contact your healthcare provider:
- Signs of Infection: If you notice any signs of infection around the ulcer, such as increased redness, warmth, swelling, or drainage of pus, it's essential to seek medical attention promptly. Signs of systemic infection, such as fever or chills, should also be addressed promptly.
- Changes in Ulcer Appearance: Any changes in the appearance of the ulcer, such as an increase in size, depth, or severity, should be reported to your healthcare provider. Also, if you notice the development of new ulcers or worsening of existing ulcers, it's important to seek medical evaluation.
- Persistent Pain or Discomfort: If you experience persistent pain or discomfort associated with the ulcer, despite appropriate wound care measures, it's advisable to contact your healthcare provider. Pain management strategies may need to be adjusted, or further evaluation may be necessary.
- Foul Odor or Unusual Drainage: A foul odor emanating from the ulcer or the presence of unusual drainage, such as thick, discolored, or malodorous discharge, may indicate infection or other complications requiring medical attention.
- Difficulty Walking or Weight-Bearing: If you experience difficulty walking or bearing weight on the affected foot due to pain, swelling, or other symptoms, it's important to seek medical evaluation to assess for underlying issues and prevent further complications.
- Development of Systemic Symptoms: Symptoms such as fever, nausea, vomiting, or confusion may indicate the presence of systemic infection or other serious complications requiring immediate medical attention.
- Poor Progress with Healing: If the ulcer does not show signs of improvement or healing despite appropriate wound care measures, it's important to consult your healthcare provider for further evaluation and management.
- History of Complications: If you have a history of complications related to diabetic foot ulcers, such as peripheral arterial disease, neuropathy, or previous amputations, it's essential to maintain regular follow-up with your healthcare provider and seek prompt attention for any new or worsening symptoms.
Our Approach
To Diabetic Foot Ulcers
At MetaCure we prioritize the well-being and comfort of our patients. Our experienced team of healthcare professionals is dedicated to providing prompt, comprehensive, and compassionate care for lacerations of all types and severities.
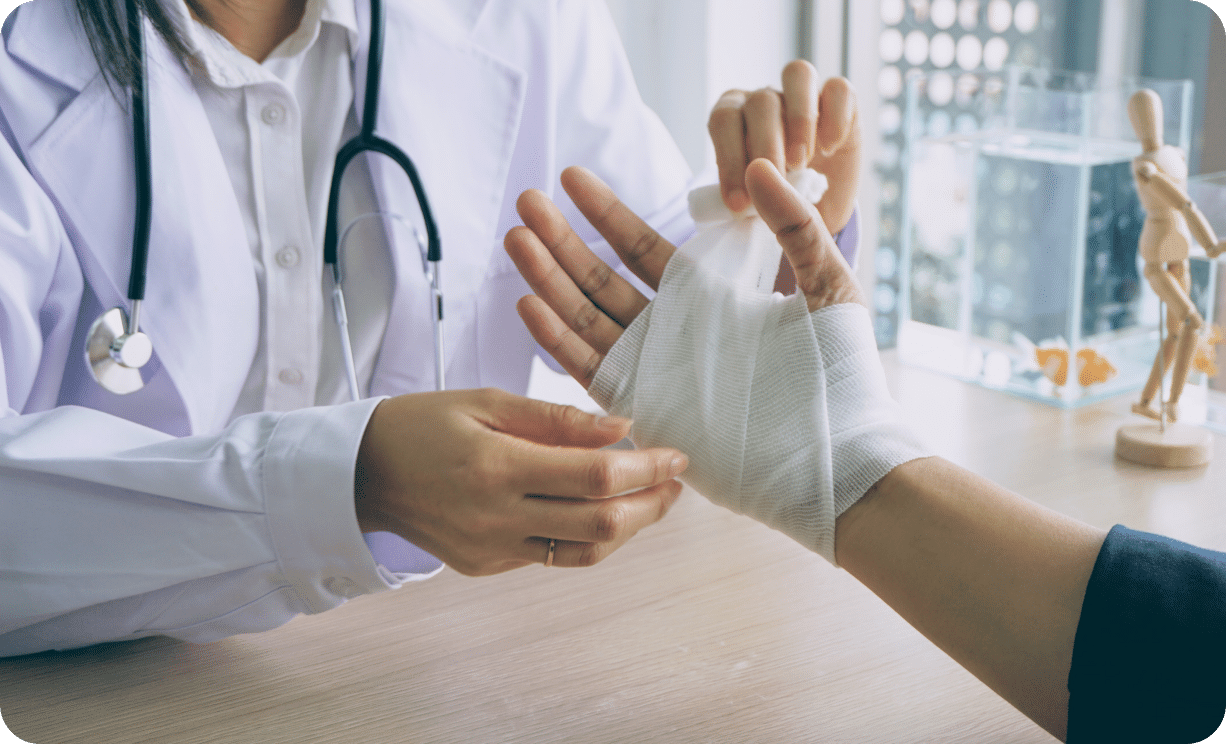
Our Diabetic Foot Ulcers Treatments
Medical treatments for diabetic foot ulcers aim to promote wound healing, prevent infection, and reduce the risk of complications.